Turbulent reactive flows mostly happen in engineering applications. For example, in combustion, where distinct species start reacting with each other during the burning process to produce heat and work, it is being used to increase the fuel efficiency and reduce soot and NOx. In this study, to overcome the closure problem in turbulent transport and chemical reaction, we applied the PDF methods to overcome the closure problem.
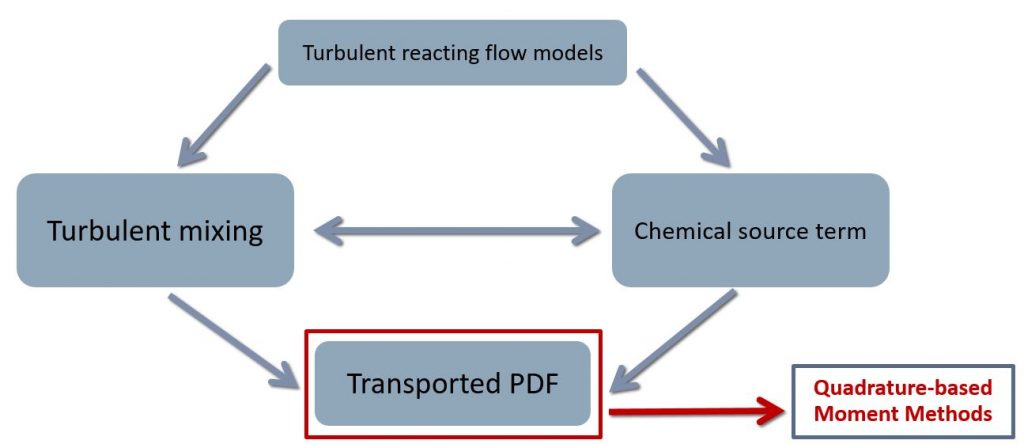
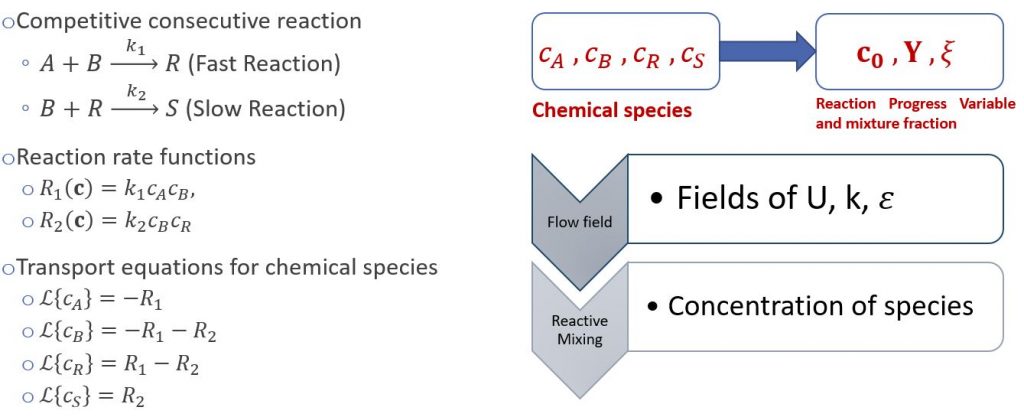
We have concluded that the advantage of using PDF method is that it provides the entire information on joint composition PDF. However, there is a need of mixing models for molecular diffusion. We validated the method using different mixing models, the one that I have developed in my previous project and the IEM model. We reduced the number of equations to be solved by introducing the transport equation based on the joint composition probability density function for the mixture fraction and reaction progress variables as internal coordinates. Later, we applied the conditional quadrature method of moments (CQMOM) to close the transport equation and remove the dependency of the solution from internal coordinates.

Conference proceedings
- Passalacqua, A., Madadi-Kandjani, E., Heylmun, J., Fox, R.O., 2016. A Conditional Quadrature Method of Moments for Turbulent Mixing Coupled to a Population Balance Equation. 9th International Conference on Multiphase Flow, At Firenze, Italy.
- Williams, D. N., Madadi-Kandjani, E., Passalacqua, A., Fox, R. O., 2015. A quadrature-based CFD model for single-phase turbulent reacting flows. AIChE Annual Meeting, At Atlanta, GA.